ORACLE EDMCS maintains the chart of accounts for an organization. An audit is required within ORACLE EDMCS to keep track of changes made to the chart of accounts and get details on when the legal entities/accounts are created. ORACLE EDMCS gives these features without coding. Auditors can generate ORACLE EDMCS audit reports to check if a company's financial statements comply with GAAP.
Why Run an Audit
An audit can be requested at any time by the management or stockholders of a company. Someone must run an audit to view who made changes to an artifact or metadata, when it was changed, and what was changed.
An audit trail is important because it's used to verify and validate all the transactions and security changes if any.
In Oracle EDMCS, an out of box audit provides the complete transaction logs at a given time and keeps track of all the user activities. It is easy to navigate, and Oracle provides an out-of-box feature. In ORACLE EDMCS, respective request IDs are attached to the audit logs; hence, any request can be tracked in detail if required.
Auditing in ORACLE EDMCS
All the companies audit metadata and hierarchy changes. It is difficult for the corporation to manage the hierarchical changes in excel and provide the same to the auditors during the audit cycle. Oracle EDMCS comes with the out-of-the-box functionality where any hierarchical change and its approval can be managed in the audit logs and retrieved easily at any given time with the required filters.
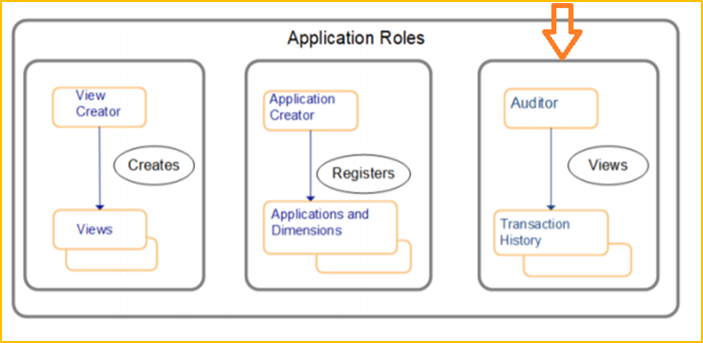
Security – Auditor Role in ORACLE EDMCS
ORACLE EDMCS has an application-level out-of-box auditor role. The auditor role lets the user view changes made to data in all applications. It does not grant the ability to make any changes to data. Thus, ORACLE EDMCS auditor role can be provided to the company auditors, who can view the transaction history by themselves and complete the audit process.
ORACLE EDMCS – Audit Overview
ORACLE EDMCS auditing feature provides visibility of all changes with audit history. It supports regulatory compliance based upon auditors' inquiries and distinguishes user errors from the system.
ORACLE EDMCS has two types of Audits:
- Auditing Transaction History
- Auditing Permissions
Auditing Transaction History
Auditing transaction history lets the Auditor view changes made to metadata over time by viewing the transactions involving that metadata. The auditor can filter the transactions based on interest. For example, auditors can view all the transactions made in the last month for a particular Account and actions for a specific hierarchy set. All the Audit logs can be downloaded into excel

To access transaction history, click the Audit card on the home page, and then select Transactions in the left panel.
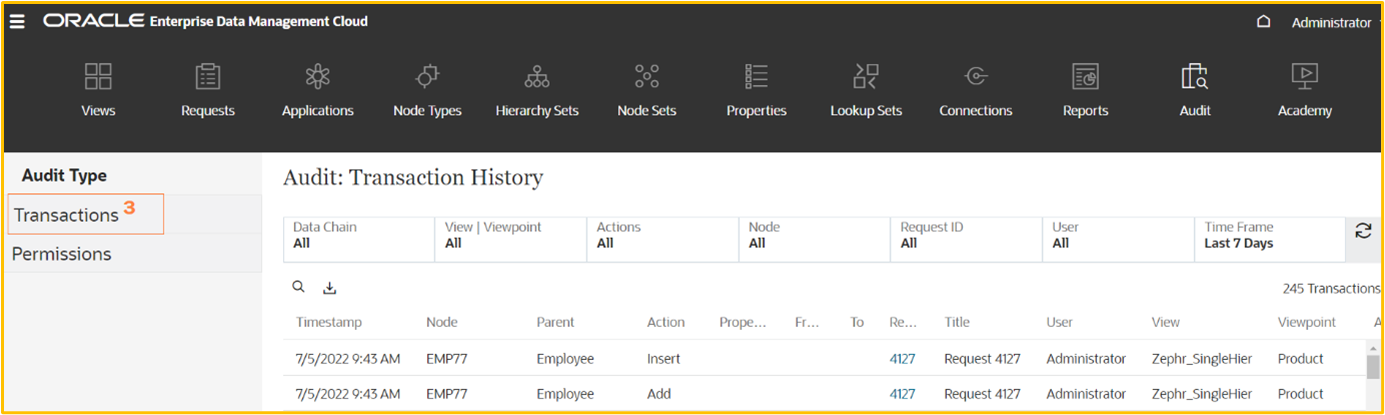
For auditing specific set of records, different type of filters can be applied.
Filters can be applied based on Data chain, View or viewpoint, Actions, Node, Request ID, User and Time frame.
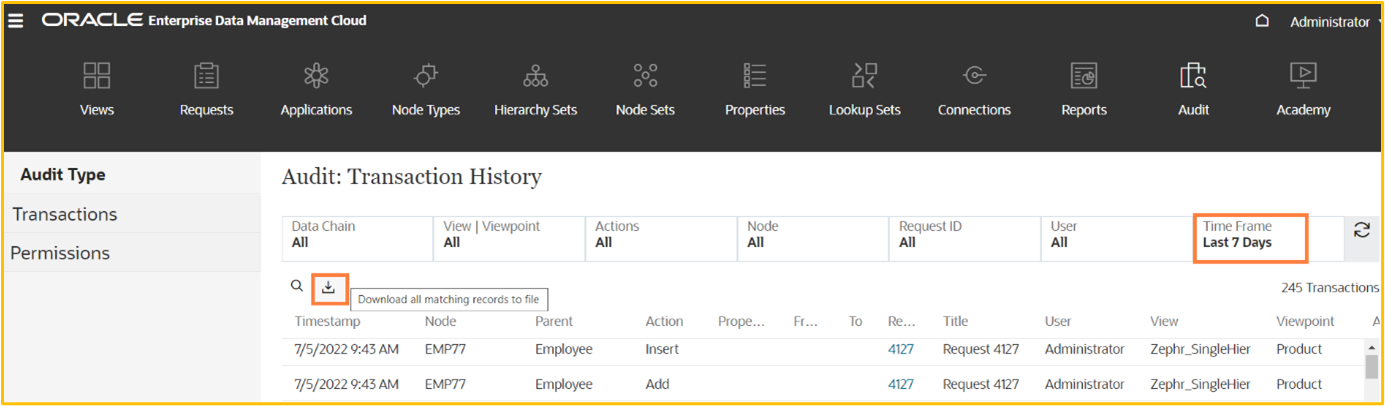
For example, apply the filter on time frame to see last 7 days of transactions and then click on the download ikon to download the last 7 days of records in an excel file.
Auditing Permissions
Auditing permissions enables you to see the changes made to permissions over time. You can filter the permissions that you want to view.
To view permission changes, click the Audit card on the home page, and then select Permissions in the Audit Type panel.
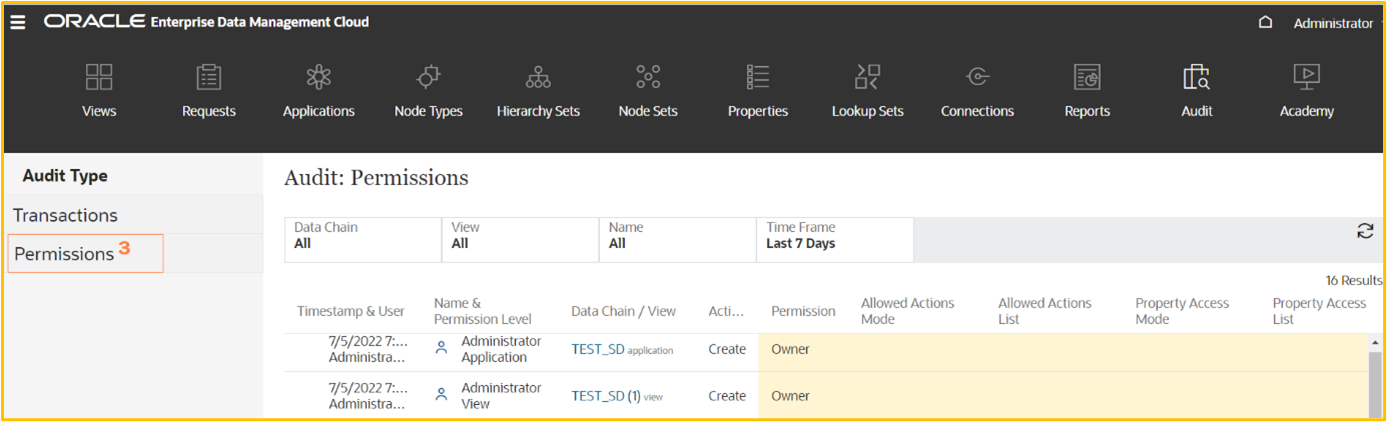
Filters can be applied to view specific permission update based on Data chain, View, Name and Time frame.
Want to Learn More?
If you would like a free consultation please contact Gerard at Redhill Business Analytics via email or the contact form below.